Reading time: approx. 5 min.
Imagine if your cannabis plants could talk – they'd tell you about their needs and deficiencies. While they can't speak, they do show you what they need through their leaves and growth patterns. This article is all about nutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants. Learn to interpret the subtle signals your plants are sending to identify and fix deficiencies early. Get ready to become a plant whisperer and save your harvest!
What are Cannabis Deficiencies?
Cannabis plants can exhibit various deficiency symptoms that arise from inadequate nutrient supply. These deficiencies can significantly impact the growth, health, and yields of the plants. It is important to recognize the signs of deficiencies early and take appropriate measures to restore the plants to a healthy state.
Table of Deficiencies and Excesses in Cannabis Plants
An overview of the most common deficiencies and excesses in cannabis plants:
Nutrient Deficiencies and Excesses
| Nutrient | Deficiency Symptoms | Excess Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N) | Yellow leaves, slowed growth | Dark green leaves, burnt leaf tips |
| Phosphorus (P) | Dark green to bluish leaves, red stems | Inhibition of calcium buildup |
| Potassium (K) | Yellow edges on older leaves, brown spots | Salt buildup on soil, stunted growth |
| Magnesium (Mg) | Yellow spots between leaf veins | Stunted leaves, dark green veins |
| Calcium (Ca) | Distorted leaves, root rot | Chlorosis on leaves, leaf necrosis |
| Boron (B) | Stunted roots and new shoots | Yellow leaf tips, dead leaf tips |
| Copper (Cu) | Wilting leaves, delayed growth | Leaf necrosis, reduced root development |
| Iron (Fe) | Yellow leaves with green veins | Bronze spots on leaves |
| Manganese (Mn) | Yellow spots between leaf veins | Dark green veins, leaf necrosis |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | Stunted plants, yellow leaves | Leaf necrosis, reduced nodule formation |
| Silicon (Si) | Weak stems, susceptible plants | Chalky leaf surfaces |
| Sulfur (S) | Yellow leaves, weak growth | Dark green leaves, burnt leaf tips |
| Zinc (Zn) | Stunted leaves, disrupted growth | Leaf chlorosis, reduced leaf size |
How to Identify and Treat Nutrient Deficiencies

Identifying and treating nutrient deficiencies is crucial for successful cannabis cultivation. Here are some steps you can follow:
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect your plants for signs of deficiencies such as discoloration, spots, or abnormal growth.
- Soil and Water Analysis: Check the pH and nutrient concentrations in the soil and water. An incorrect pH can affect nutrient uptake.
- Adjust Nutrient Solutions: Use specific nutrient solutions to correct deficiencies. Be careful not to over-fertilize to avoid excesses.
- Foliar Spray: For acute deficiencies, a foliar spray can provide quick relief. This method allows direct nutrient absorption through the leaves.
Common Problems with Cannabis Plants
Identifying and correcting nutrient deficiencies is crucial for the healthy growth and productivity of cannabis plants. The most common and important deficiencies include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, calcium, boron, copper, iron, manganese, molybdenum, silicon, sulfur, and zinc. Each of these nutrients plays a vital role in the growth process and overall health of the plants. A deficiency in any of these nutrients can significantly impact the growth and vitality of the plants. The following sections detail the most common deficiencies and their treatments:
Nitrogen (N)

Nitrogen is an essential macronutrient for the growth of cannabis plants. A deficiency is indicated by yellow leaves and stunted growth. To treat nitrogen deficiency, you can use a nitrogen-rich fertilizer and ensure the soil pH is within the optimal range. ➜ More on Nitrogen deficiency in cannabis plants
Phosphorus (P)
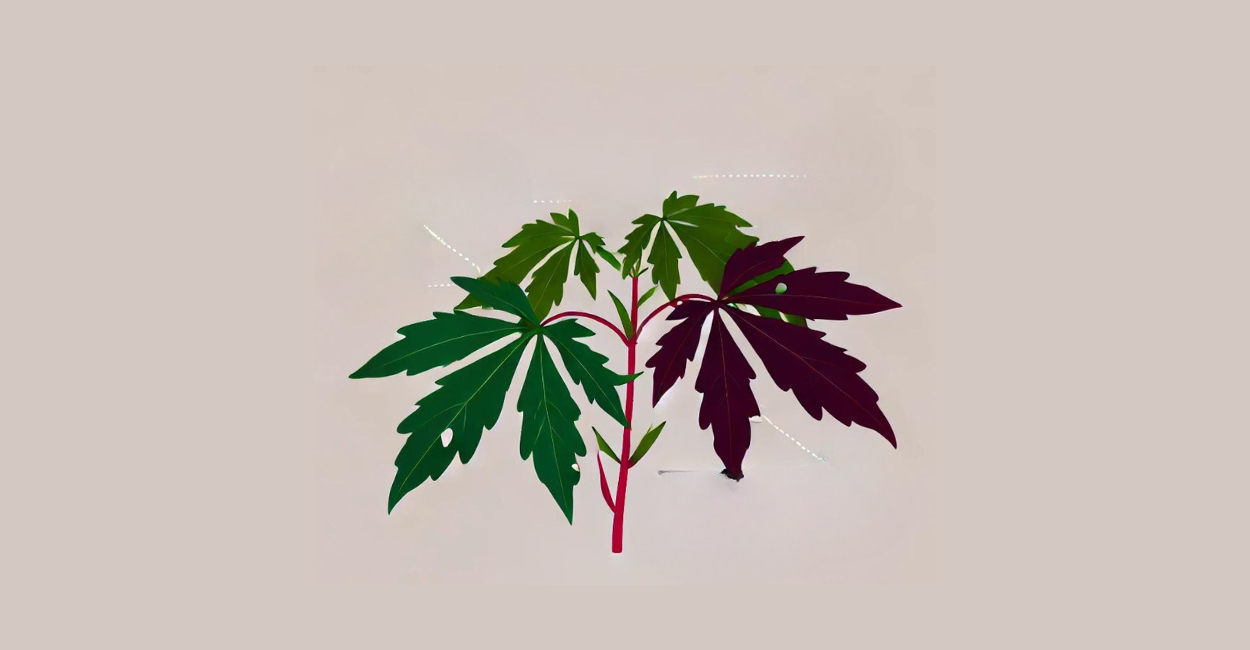

Phosphorus is vital for energy transfer in plants. A deficiency is manifested by dark green to bluish leaves and red stems. Adding phosphorus-rich fertilizer and controlling the pH can help correct this deficiency. ➜ More on Phosphorus Deficiency in Cannabis Plants
Potassium (K)
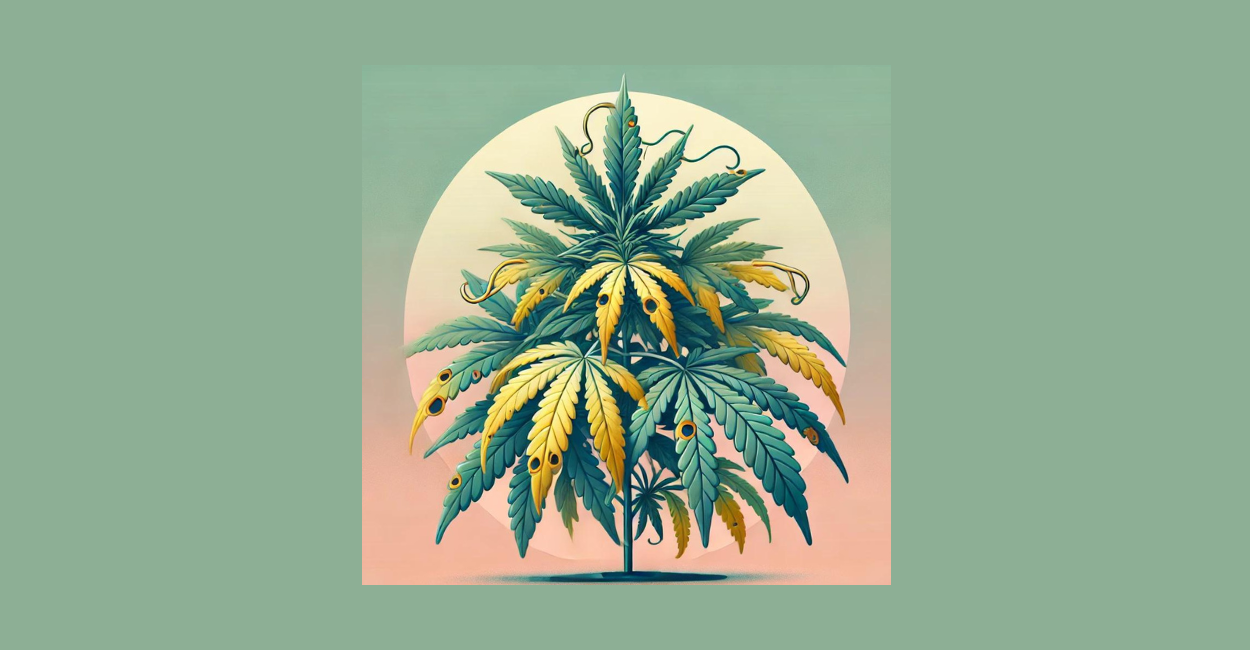

Potassium aids in water uptake and enzyme activity in plants. A deficiency results in yellow edges on older leaves and brown spots. Using a potassium-rich fertilizer and maintaining the correct pH can solve this issue. More on this soon. ➜ More on Potassium Deficiency in Cannabis Plants
Magnesium (Mg)

Magnesium is a key component of chlorophyll and necessary for photosynthesis. A deficiency causes yellow spots between the leaf veins. Adding magnesium-rich fertilizers and controlling the pH are effective measures for treatment. ➜ More on Magnesium Deficiency in Cannabis Plants
Calcium (Ca)

Calcium is important for cell wall structure and root development. A deficiency is indicated by distorted leaves and root rot. Calcium-rich fertilizers and monitoring the pH can help remedy this deficiency. ➜ More on Calcium Deficiency in Cannabis Plants
Boron (B)

Boron is an essential micronutrient for the growth of cannabis plants. A deficiency can lead to stunted roots and new shoots. Adding boron-rich fertilizers can correct this problem. ➜ More on Boron Deficiency in Cannabis Plants
Copper (Cu)

Copper is important for photosynthesis and the plant's metabolism. A deficiency results in wilted leaves and delayed growth. Copper-containing fertilizers can help address this deficiency. ➜ More on Copper Deficiency in Cannabis Plants
Iron (Fe)

Iron is necessary for chlorophyll formation and plant respiration. A deficiency is indicated by yellow leaves with green veins. Iron chelates can help treat this deficiency. ➜ More on Iron Deficiency in Cannabis Plants
Manganese (Mn)

Manganese is vital for photosynthesis and nitrogen metabolism. A deficiency results in yellow spots between the leaf veins. Manganese-containing fertilizers can solve this problem. ➜ More on Manganese Deficiency in Cannabis Plants
Molybdenum (Mo)

Molybdenum is an essential micronutrient for nitrogen fixation. A deficiency can cause stunted plants and yellow leaves. Molybdenum-containing fertilizers can help correct this deficiency. ➜ More on Molybdenum Deficiency in Cannabis Plants
Silicon (Si)
![]()
Silicon strengthens cell walls and increases disease resistance. A deficiency can result in weak stems and susceptible plants. Silicon-containing fertilizers can remedy this problem. More on this soon. ➜ More on Silicon Deficiency in Cannabis Plants
Sulfur (S)

Sulfur is important for the formation of amino acids and proteins. A deficiency results in yellow leaves and weak growth. Sulfur-containing fertilizers can help address this deficiency. ➜ More on Sulfur Deficiency in Cannabis Plants
Zinc (Zn)

Zinc is necessary for the plant's growth hormone. A deficiency is indicated by stunted leaves and disrupted growth. Zinc-containing fertilizers can help correct this problem. ➜ More on Zinc Deficiency in Cannabis Plants
How to Keep Cannabis Plants Healthy

To keep cannabis plants healthy, we recommend paying attention to the following aspects:
- Optimizing Growing Conditions: Ensure optimal temperature, humidity, and ventilation.
- Nutrition: Use balanced nutrient solutions and monitor the pH of the water.
- Water Intake: Ensure plants receive adequate but not excessive water.
- Pest Control: Regularly inspect your plants for signs of diseases, mold, and pests.
- Soil vs. Hydroponics: Choose the right growing method for your needs and optimize it accordingly.
- Compost and Mycorrhizae: Use organic additives to improve soil health.
Important Note:
Ensuring your cannabis plants receive the right nutrients is crucial for their overall health and productivity. If you observe deficiency symptoms such as discoloration, stunted growth, or poor yield, you should reassess and adjust your nutrient program. Adding specific nutrients or supplements can help rectify deficiencies. Always monitor the pH levels of your soil or growing medium, as an incorrect pH can inhibit nutrient uptake. For more information and suitable products to address nutrient deficiencies, visit our Cannabis Plant Nutrient Products Category.
Proper care and nutrition of cannabis plants are essential for healthy growth and high yields. By early identification and treatment of nutrient deficiencies and optimizing growing conditions, you can ensure your plants reach their full potential. Utilize available resources and tools to enhance your cannabis cultivation skills and achieve successful harvests.
Disclaimer
This website's content is for informational use only and should not be considered medical or legal advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for health-related issues. Be aware of local regulations regarding cannabis cultivation. We are not liable for any actions taken based on this information.